How to Use Lucien - Your Quick Start Guide
Welcome to Lucien — AI research assistant that helps analyze complex datasets, generate hypotheses, design and execute experiments.
This guide will help you get started in just a few steps.
![]()
 Download & Install
Download & Install
Get the latest installer from the Lucien Downloads Page.
Disclaimer: By using Lucien, you acknowledge that you have read and agree to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy from above link.
Mac
Expand mac Installation details
Download-
Download the
.dmginstaller for Mac. -
Open the downloaded file and drag Lucien into your Applications folder.
-
Double-click to launch.
Windows
Expand window Installation details
Download-
Download the
.exeinstaller for Windows. -
Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions.
-
Launch Lucien from the Start Menu or Desktop.
Windows Warning: It’s Safe to Proceed!
This is expected for new apps. Click “Keep anyway” and then “Run anyway” to continue.
Linux (Debian-based)
Expand linux Installation details
Download-
Download the
.debinstaller for linux. -
Open a terminal and install:
sudo dpkg -i path/to/lucien-desktop.deb sudo apt-get install -f -
Launch Lucien from your application menu.
 Note for WSL Users
Note for WSL Users
Lucien requires a browser to complete the login process. You can install Chrome with:cd /tmp wget https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb sudo apt install -f ./google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb
![]()
 Sign In
Sign In
Lucien is currently in closed beta, available only to allowlisted users.
- Sign up using your allowlisted email address. Please refer to this signup guide for detailed steps
- Log in with your account to start using Lucien.
![]()
 Local Env Setup
Local Env Setup
To enable most advanced features, Lucien needs to set up a local execution environment.
view local env installation details
- When you first open Lucien, installation begins automatically.
- This process can take 5–10 minutes, depending on your system and network speed.
What to do:
- Wait until installation finishes.
- Do not close the app during setup.
- Restart Lucien once complete.
![]()
Core Concepts
Workspace
A Workspace serves as the top-level organizational container for projects in Lucien. It defines the working environment with a specific directory path, workspace-level system prompts, and execution settings. Each workspace acts as a project boundary that contains sessions, knowledge sources, and configuration settings, providing consistent context for all AI interactions within that project scope.
Knowledge Source
Knowledge Sources let you connect Lucien to your documents and files. Lucien will intelligently search and reference this information to provide accurate, current responses tailored to your specific needs. They represent the application’s knowledge management system, where users can upload various file types that get processed, indexed, and made searchable. Each knowledge source includes metadata like summaries, token counts, and file type information, allowing the AI to reference specific documents during conversations.
Session
A Session represents an individual conversation thread or chat instance within a workspace. Each session maintains its own conversation history, name, and can be associated with specific agents, canvases, and todo lists. Sessions are the active conversation contexts where users interact with the AI, and multiple sessions can exist within a single workspace for different conversation topics.
Skills
Skills are reusable AI personas or behavioral configurations that define how Lucien should respond and what capabilities it can access. They act as templates that include custom prompts, tool access permissions, and specialized behaviors for specific domains or tasks. Skills can be built-in, user-created, or shared between users, and they determine which tools the AI can use during conversations. You can explore skills shared by others in our skill store.
Tools
Tools are external functionalities that extend Lucien’s capabilities through the Model Context Protocol (MCP). They provide dynamic actions like file operations, code execution, web browsing, or integration with external services. Tools can be workspace-specific built-ins (like Jupyter notebooks) or external MCP server tools, and their availability is controlled by workspace settings and skill
configurations.
![]()
 Key Features
Key Features
Creating a New Workspace
- From the Sidebar: Click + New workspace, enter a name, and create.
- From Main Area: Click the New Workspace card, enter a name, and create.
Working in a Workspace
1. Create a new session
-
Ask Questions: Enter your request in the input bar.
-
Attach Files: Click
 to upload files (images, PDFs, Excel, etc.).
to upload files (images, PDFs, Excel, etc.). -
Skills: Task-specific workflows with tools/models/prompts.
- Built-in:
- Deep Research – generates a comprehensive research report.
- Slides Generation – creates an HTML presentation.
- Custom: Create your own or share with others.
- Built-in:
-
Permissions: Control what Lucien’s agents can do.
- Follow default rules = requires approval for risky tools.
- Always ask = Lucien requests approval every time.
- Always allow = Lucien can use tools automatically.
2. Workspace Prompt
-
Purpose: Define a system prompt/context for all requests in this workspace.
-
When to Use:
- Keep responses aligned with project goals.
- Provide background details so you don’t repeat them.
-
You can also set a global prompt in settings.
3. Local Working Directory
-
Purpose: Lets Lucien access and work with local files.
-
How to Set:
- Click Set in Execution environment.
- Choose the folder with project files.
- Confirm selection.
-
Notes: Only files in this folder/subfolders are accessible.
4. Code Execution
- Enable/Disable: Control whether code execution is allowed.
- Open JupyterLab: For advanced coding, notebooks, and file manipulation.
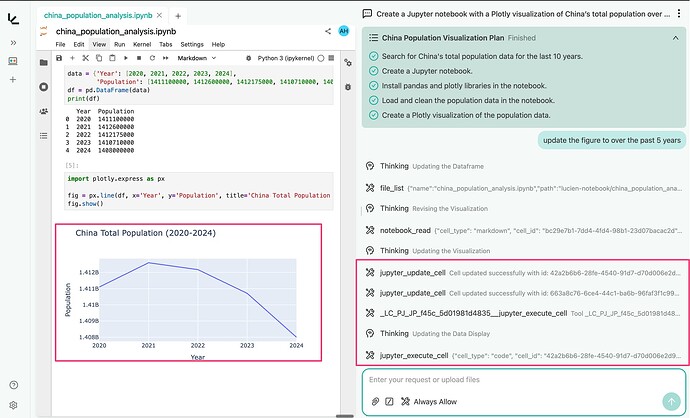
📘 Example: Collaborating with AI in Jupyter Notebooks
-
Create a Notebook
- Ask: “Create a Jupyter notebook with a Plotly visualization of China’s total population over the past 20 years.”
- AI sets up notebook, installs libraries, loads data, and generates chart.
-
Refine or Extend Your Analysis
- Ask: “Update the figure to cover the past 5 years.”
- AI updates DataFrame and redraws chart.
For more details, please refer to the Mcp embedded resources usage guidance
5. Session Management
- Session: Displays all chat sessions.
- Canvas: View Markdown, Notebook, and HTML canvases.
- Knowledge Source: Upload reference files to improve Lucien’s responses.
![]()
 Settings
Settings
Click your name in the bottom-left corner of the sidebar to open Settings.
Model & System Prompt
Choose the AI model you prefer and define Lucien’s behavior and response context.
Skills & Tools
-
Skills
- Built-in: Deep Research, Slides Generation.
- Custom: Use + Add Skill to create a custom skill tailored to your needs. Please test the skill in a session to ensure it behaves as expected. You can also share your skill with others by clicking the Share button to generate a shareable URL.
- Import Shared Skill: When you receive a shared skill link, paste it into the Import Shared Skill dialog. Lucien will automatically configure all settings included in the skill, along with any required MCP servers.
-
MCP Servers
-
Add from MCP Store: https://mcpm.sh/registry/?source=lucien&protocol=lucien
-
Import DXT or add manually.
Import from config json in other apps (Claude Desktop / Claude Code / Cursor / ...)
The json usually contains ‘command’, ‘args’ and ‘env’ field, e.g:
... "mcpServers": { "some-server": { "type": "stdio", "command": "npx", "args": [ "package_name" ], "env": {} } } ...Just extract value of these fields and input them in corresponding field in Lucien settings.
On Windows, please use slash(
/) instead of backslash(\) for splitting the file path. -
- Support for long-running operations with progress notifications.
- Debug: “Open Logs Folder” in Advanced settings.
Advanced Settings
- Executable: Shows versions of installed CLI tools.
- Import/Export: Backup or restore settings.
- Logs: Access logs for troubleshooting.
![]()
 FAQ & Support
FAQ & Support
 FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Report bugs: Create a topic in the Lucien category
Report bugs: Create a topic in the Lucien category Feature requests: Share your ideas in the Feedback category
Feature requests: Share your ideas in the Feedback category Contact: support@pathintegral.xyz
Contact: support@pathintegral.xyz
![]()
 You’re Ready!
You’re Ready!
That’s it! You’re now set up to explore everything Lucien can do. Dive in, experiment, and let Lucien support your journey.